tree in bud opacities causes
TIB opacities are most often a manifestation of infections or aspiration and patterns of disease can provide clues to the most likely diagnosis. Another important entity that can produce the tree-in-bud pattern is bronchioalveolar carcinoma BAC 1.
We here describe an unusual cause of TIB during the COVID-19 pandemic.
. Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases. TIB opacities are also associated with bronchiectasis and small airways obliteration resulting in mosaic air trapping. Studies have reported that pulmonary TB accounts for only 28 of the cause of tree-in-bud opacities as opposed to pulmonary apical granulomas and fibrosis being more suspicious of the disease 10.
Cardasis JJ MacMahon H Husain AN. Thus if other causes of TIB opacities remain constant the relative incidence of viral infections as a cause of TIB opacities could range from as low as 3 five of 166 to as high as. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. A young male patient who had a history of fever cough and respiratory distress presented in the emergency department. Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a subset of centrilobular nodules.
Other known malignancies include breast liver stomach prostate and ovarian cancer as well as Ewings sarcoma. Ann Am Thorac Soc. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated.
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. Originally and still often thought to be specific to endobronchial Tb the sign is actually non-specific and is the manifestation of. Causes and imaging patterns of tree-in-bud opacities.
This tree-in-bud pattern is due to the presence of caseation necrosis and granulomatous inflammation within and surrounding the terminal and respiratory bronchioles and. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. Respiratory infections 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65 of 166 39 bacteria 44 of 166 27 viruses.
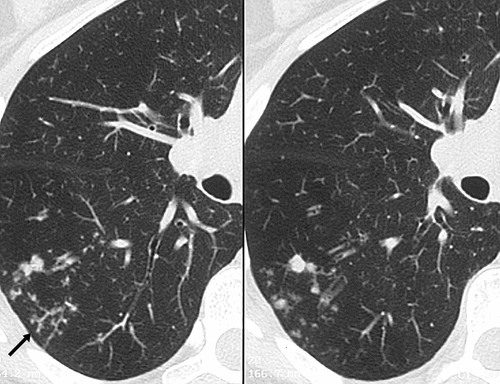
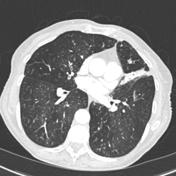
11 TIB opacities represent a central imag- Background. The most common CT findings are centrilobular nodules and branching linear and nodular opacities. Tree in bud opacification refers to a sign on chest CT where small centrilobular nodules and corresponding small branches simulate the appearance of the end of a branch belonging to a tree that is in bud.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. TIB opacities typically show branching. The most common CT findings are centrilobular nodules and branching linear and nodular opacities.
Respiratory infections 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65 of 166 39 bacteria 44 of 166 27 viruses. Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated.
Typical findings of BAC on HRCT include a solitary nodule or mass 43 focal or diffuse consolidation 30 or. The classic cause of the tree-in-bud pattern is postprimary tuberculosis. The purpose of this study was to.
As in this case renal cell carcinoma is one of the most common malignancies that may produce this vascular cause of tree-in-bud pattern. The spectrum of lung disease due to chronic occult aspiration. And 20 viral infections annually that showed TIB opacities on CT scans.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. The tree-in-bud pattern suggests active and contagious disease especially when associated with adjacent cavitary disease within the lungs. Causes and imaging patterns of tree-in-bud opacities.
Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases. Tree-in-bud TIB appearance in computed tomography CT chest is most commonly a manifestation of infection. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated.
BACKGROUND Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. 3 found that the tree-in-bud pattern was seen in 256 of the CT scans in patients with bronchiectasis. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of TIB opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with TIB opacities.
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Ct Scan Of Chest Revealing Scattered Tree In Bud Opacities In Both Download Scientific Diagram

Chest Ct With Multifocal Tree In Bud Opacities Diffuse Bronchiectasis Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Pdf Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Semantic Scholar

Ct Scan Of The Chest Axial View With Tree In Bud Opacities Bilateral Download Scientific Diagram
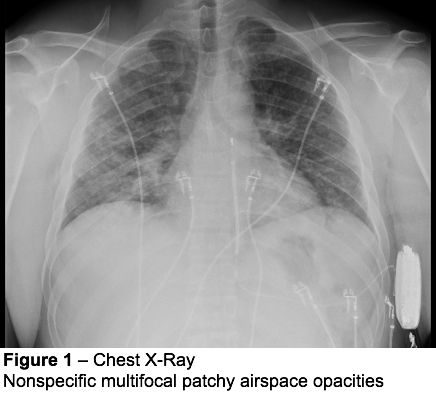
It Is Not Always Tuberculosis Tree In Bud Opacities Leading To A Diagnosis Of Sarcoid Shm Abstracts Society Of Hospital Medicine
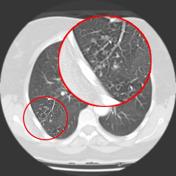
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles
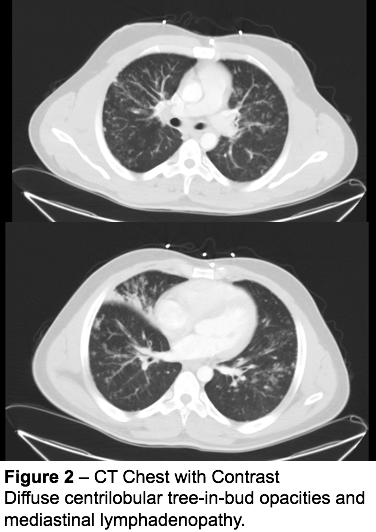
It Is Not Always Tuberculosis Tree In Bud Opacities Leading To A Diagnosis Of Sarcoid Shm Abstracts Society Of Hospital Medicine
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Pin By Susan Emerson On Flash Cards Science Biology Medicine Radiography

Pin By Ladislav Ruzicka On Medicine Radiology Imaging Radiology Medical Radiography